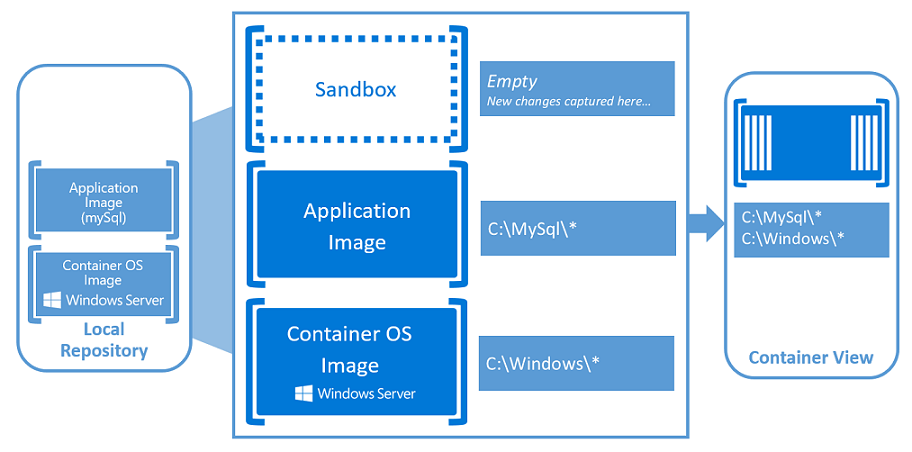
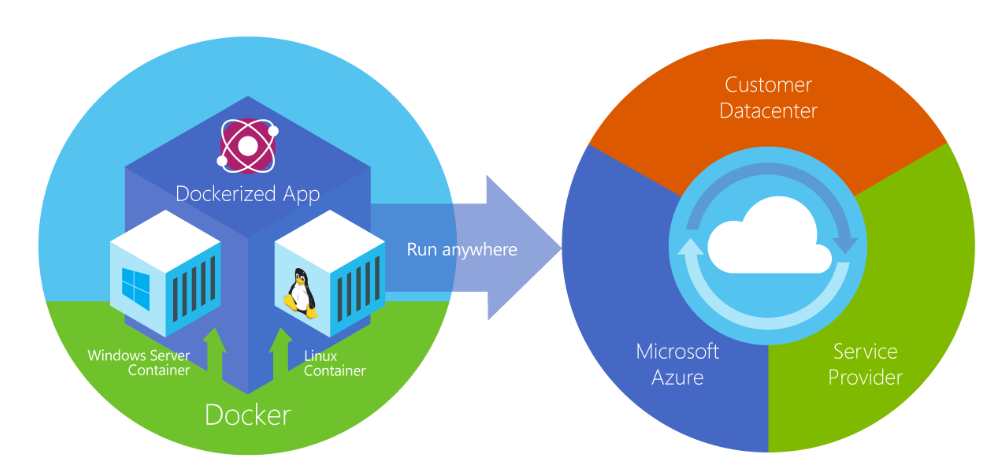
Move or extend on-premises VMware environments to Azure
Seamlessly move VMware-based workloads from your data centre to Azure and integrate your VMware environment with Azure. Keep managing your existing environments with the same VMware tools you already know while you modernise your applications with Azure native services. Azure VMware Solution is a Microsoft service, verified by VMware, that runs on Azure infrastructure.
You can read more here https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/services/azure-vmware/